U.S. B2B Exhibition Industry Faced Minor Slowdown Q2 2024

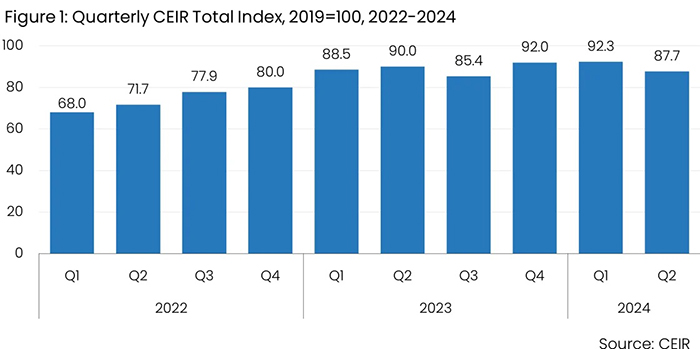
The U.S. B2B exhibition industry experienced a minor slowdown following a robust first quarter (Q1) in 2024, according to the Center for Exhibition Industry Research (CEIR) Q2 2024 Index that measures overall exhibition performance by four metrics—exhibitors, attendance, net square footage and real revenues.
Due to a modest performance in all four of the CEIR metrics for completed events, the Q2 Index value dropped from 92.3 in Q1 to 87.7 in Q2, compared to 100 in 2019.
Marsha Flanagan, president and CEO of IAEE, said the latest CEIR data demonstrates the B2B exhibition industry is making steady progress in its recovery, with key metrics all trending in the right direction—but at varying paces.
“We remain cautiously optimistic about the industry’s ability to fully rebound to pre-pandemic levels in the near future,” Flanagan said.
The health of the U.S. exhibitions sector will undoubtably be impacted the U.S. economic outlook.
“Economic growth is expected to be slower next year, but with strong household balance sheets, a gradual upswing expected in business investment, and moderating inflation, we anticipate a favorable context for moderate exhibition sector growth,” said Adam Sacks, president of Tourism Economics, a subsidiary of independent global advisory firm Oxford Economics.
He added that while the recovery of the exhibition sector has been an uneven one, the economic environment should support further improvements.
 What else does the CEIR data reveal? Here’s our curated list of four takeaways from CEIR’s latest Index report:
What else does the CEIR data reveal? Here’s our curated list of four takeaways from CEIR’s latest Index report:
- Slower growth than this time last year. This decline reflects a 2.3 percentage point decrease compared to Q2 2023.
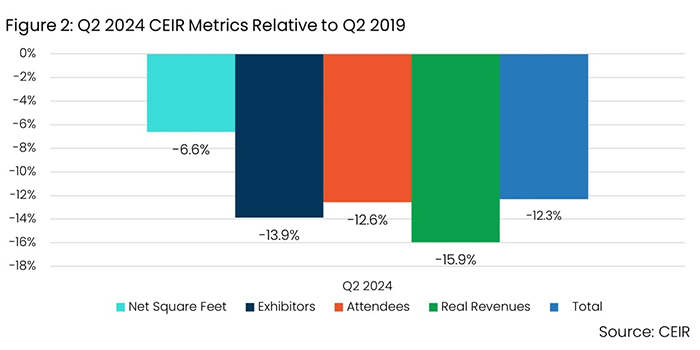
- Not all are back to 2019 levels yet. Performance remains 12.3% below the same period in 2019, indicating a modest setback from last year’s figures, which included a 10% shortfall in Q2 2022.
- But nearly half have beat pre-pandemic numbers. Despite the downturn relative to Q1 2024, 44.3% of events in the Index sample surpassed their pre-pandemic CEIR Total Index performance, a significant increase from just 20.5% in Q2 2023.
- Show cancellations remain low. The cancellation rate for in-person events remained low at 1.0%, consistent with the same quarter in 2023 and significantly lower than the 2.2% cancellation rate in Q2 2022.
Behind the numbers: Economic Indicators
 The CEIR Index results align with overall economic performance, which indicates a slowdown without signs of recession. Consumer confidence has softened, and business sentiment has fluctuated due to recent events that have generated unwarranted pessimism about the economy, according to the report.
The CEIR Index results align with overall economic performance, which indicates a slowdown without signs of recession. Consumer confidence has softened, and business sentiment has fluctuated due to recent events that have generated unwarranted pessimism about the economy, according to the report.
The unemployment rate rose to 4.3% in July, up from 3.5% last year, primarily driven by an increase in the labor force participation rate, which is expected to alleviate wage and inflation pressures. GDP growth accelerated to 2.8% in Q2, signaling strength in the economy and improving the outlook for the CEIR Index in the second half of the year.
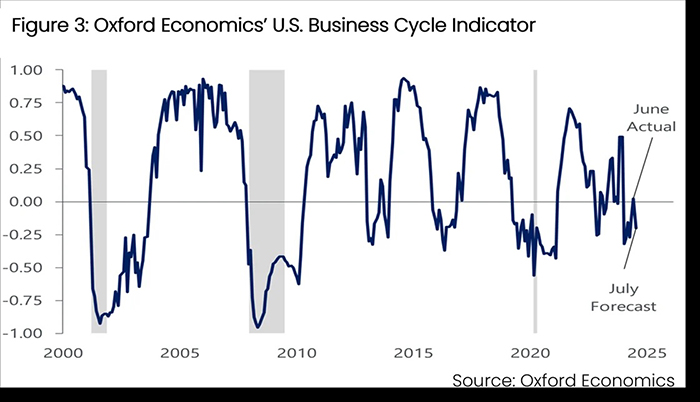
Oxford Economics’ business cycle indicator (BCI) remains in “slowdown” territory but is still well above recession levels (Figure 3). While manufacturing remains soft and housing market activity continues to be subdued due to elevated interest rates, some pressures may ease as the Federal Reserve begins its rate-cutting campaign this month.
Although it will take time for reduced borrowing costs to impact the sectors, short-term benefits from fiscal policy and the conclusion of the destocking cycle are expected to bolster business activity, according to the report.
 Consumer Spending and Travel Trends
Consumer Spending and Travel Trends
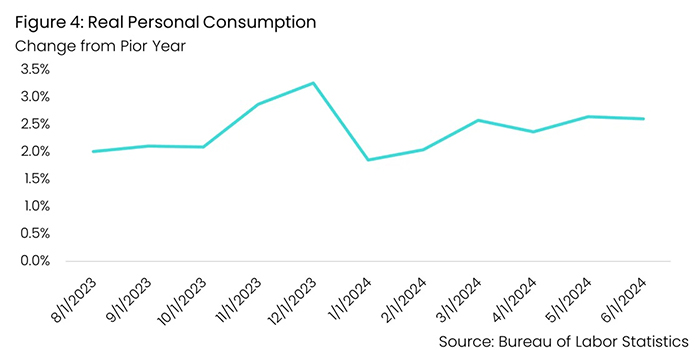
Consumer spending experienced significant growth in June, with projections for ongoing increases throughout the year as real income improves alongside robust household balance sheets, despite a rise in the unemployment rate.
Despite a decline in gas station sales due to lower gas prices and a cyberattack on auto dealerships impacting auto sales, spending in nearly all other categories increased significantly, with strong underlying retail sales in June suggesting real consumer spending in Q2 rose close to 2% annualized.
Although airline travel volumes have surpassed pre-pandemic levels, U.S. hotel demand has plateaued at about 2% below pre-pandemic levels. The increase in U.S. citizens traveling internationally has contributed to this slower recovery, with international tourist arrivals still not reaching pre-pandemic levels, resulting in a net loss of about 3% in U.S. hotel demand.
Don’t miss any event-related news: Sign up for our weekly e-newsletter HERE, listen to our latest podcast HERE and engage with us on LinkedIn!


Add new comment